Planet and People Connection

Planet and People Connection
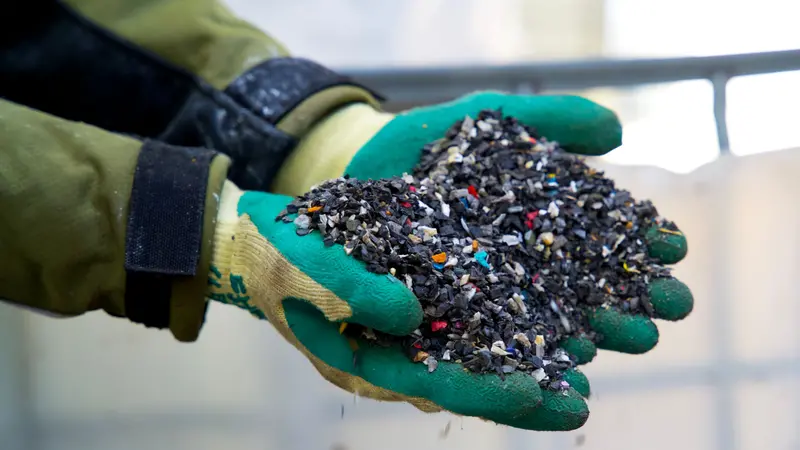
Hazards Found in Recycled Plastics
The study focused on chemicals in reusable and/or recyclable plastic food containers, such as packaging and other plastic items that come into contact with food, like kitchen utensils, plates, cups, containers. baby bottles, water dispensers, and tubing of milking machines. These items are often used in repeated contact with food and are a source of chemicals that migrate into foodstuffs. Common plastic polymers used to make these items are polyamide, polypropylene, polycarbonate, melamine resin and polyvinylchloride. A special focus is given to recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastics, which are typically used in single-use packaging.
The study authors write that “there is concern about the adverse health impacts of chemical migration when almost the entire population is ingesting plastic-associated chemicals that are often not studied adequately for their health risks.”
REFERENCES
Geueke, B., et al. (2023, May 22). Hazardous chemicals in recycled and reusable plastic food packaging. Cambridge Prisms: Plastics. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/cambridge-prisms-plastics/article/hazardous-chemicals-in-recycled-and-reusable-plastic-food-packaging/BBDE514AAFE9F1ABB3D677927B343342


 By
By