Natural Pets
Natural Pets
Outdoor Safety for Pets: Helpful Tips to Navigate Hazards
by Paige Cerulli
With nicer spring weather, pets will likely spend more time outside. Whether lounging in the backyard, taking a walk around the neighborhood or venturing out to a dog park, our awareness of potential dangers is important. Despite the risks, there is no reason to keep pets cooped up. With diligence, protecting our furry best friends can become second nature as we safely enjoy the great outdoors together with our pets.
Home and Yard
A fenced yard might seem like a safe space for pets, but that is not always the case. “Pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers are just a few of the toxic substances that could be in a pet owner’s yard,” explains veterinarian Alex Schechter, of Burrwood Veterinary, in Royal Oak, Michigan. “These substances can harm dogs and cats if they are consumed or come into contact with a pet’s skin.”
A 2013 study published in Environmental Research found that dogs exposed to professionally applied lawn care pesticides had a 70 percent higher risk of developing canine malignant lymphoma than dogs that were not exposed to these products.
Schechter recommends that pet owners choose non-chemical lawn management methods that are safe for pets, like neem oil or diatomaceous earth. “Reduce the use of chemicals by using organic farming practices or natural fertilizers,” he says.
Veterinarian Dwight Alleyne, an advisor at Betterpet, cautions that a yard might be home to plants that are poisonous to pets. “Some of these plants could include lilies, sago palms, tulips and oleander,” he advises. “It is important for pet owners who have a backyard to be able to identify any potential hazards before leaving their pet out unattended.”
Neighbors’ Yards
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, mouse or rat poison is a popular pest control choice that kills by causing excessive bleeding. Use of this product can be extremely dangerous to pets if they ingest either a poisoned rodent or the poison itself. Schechter warns, “If you see bait stations or dead rats, those areas may have been treated with a rodenticide.” He advises pet owners to have a conversation with their neighbors, suggesting the use of snap or electronic traps as more humane and less toxic alternatives.
Driveways
Coal tar sealants used on driveways contain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) that, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, may pass through skin or be inhaled. In large amounts, PAHs can irritate eyes and breathing, and several PAHs are carcinogenic in humans. Avoid sealing driveways with any coal tar products. When out for walks, pet owners should keep their dogs off other driveways, as well.
Outdoor Excursions
Dog parks carry several risks, including exposure to intestinal parasites. A 2020 study found that 85 percent of the 288 dog parks sampled had at least one dog infected with gastrointestinal parasites like Giardia, hookworms, whipworms or roundworms. These parasites can be transmitted when dogs eat or sniff poop.
“It is recommended that your dog is on a monthly heartworm preventative, which can help protect against common parasites that they may encounter,” says Alleyne. If a dog regularly visits dog parks, a vet can perform a fecal exam to identify and treat any intestinal parasites that the dog may have contracted.
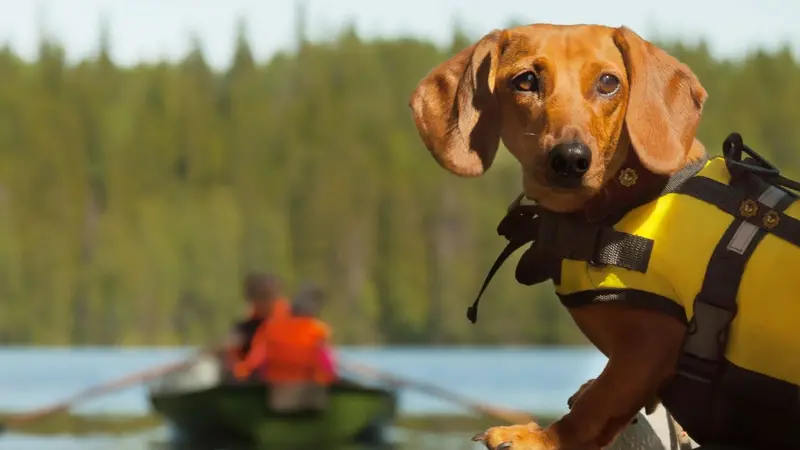
When visiting ponds and lakes, beware of blue-green algae bacteria, which commonly proliferate in freshwater bodies, particularly during summer months. Dogs can ingest algae by playing in or drinking the water, or when licking their paws. In large quantities, algae can be toxic to dogs (and humans). Because algae are not always visible, keeping dogs leashed around bodies of freshwater is best.
Paige Cerulli is a freelance writer in Western Massachusetts specializing in the health and care of pets.
Original article published at Natural Awakenings


 By
By