
Chronic Conditions and Diseases

Chronic Conditions and Diseases
Early Signs of Celiac Disease Found in the Mouth
Could oral health issues be caused by reactions to gluten? The mouth contains the second largest and most diverse microbiome, and poor oral health is associated with a number of health conditions including Celiac disease (the autoimmune disease triggered by eating gluten) and gluten sensitivity.
The gut shares the same lining, structure and immune system as the mouth. If you have chronic oral health problems, gluten may be the cause.
Here are some oral health symptoms that might be early signs of an undiagnosed gluten sensitivity.
Mouth Sores
Canker sores or mouth sores (aphthous ulcers) on the inside of the cheeks or at the edge of the mouth (angular cheilitis) are common in Celiac disease, especially after eating something sour or salty. Don’t ignore this painful symptom or immediately attribute it to eating too much citrus—the sores may be caused by Celiac disease.
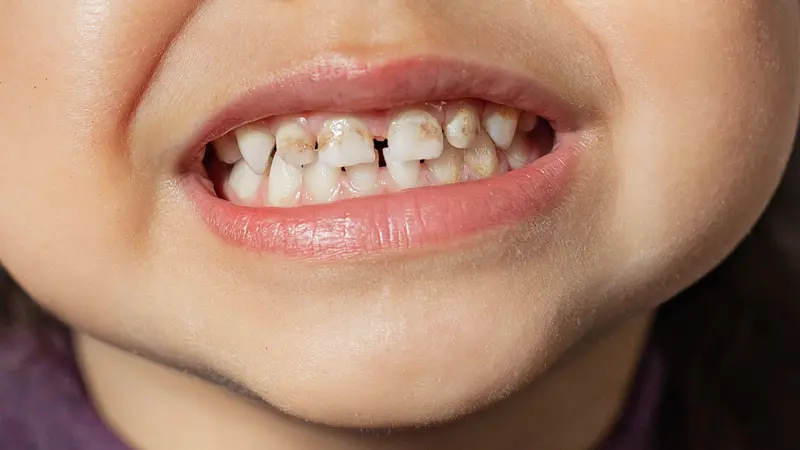
Tooth Enamel Issues
Eighty-five percent of people with Celiac disease have tooth enamel defects, or hypoplasia. This could look like discolored (yellow or brown) teeth, or teeth with white, brown, or yellow spots on them. There also may be pits in the teeth or bands across them, or the enamel may be mottled or look translucent.
Celiac Tongue
Celiac tongue will look smooth or slick, and won’t have the typical little bumps or crease down the middle. Called atrophic glossitis, a swollen, red, smooth tongue can make it painful to swallow or eat. Another common tongue issue with Celiac disease is geographic tongue, where the tongue has color-delineated shapes on it like a world map.
Inflamed Mouth Lining
Celiac disease may cause inflammation of the lining of the mouth (oral mucosa), which is known as oral lichen planus. This can look like white patches, redness, or swelling, and cause the mouth to feel sensations of pain, discomfort, or burning.
Oral Cancers
People with Celiac disease who don’t strictly avoid gluten have higher rates (estimated to be 10x higher) of head and neck cancers than those who follow a gluten-free diet. Cancers of the mouth, esophagus, larynx, and lymphoma are more common in untreated Celiac disease.
Mouth Symptoms in Children
In children with undiagnosed Celiac disease, mouth symptoms could include:
- Burning tongue
- Delayed tooth eruption
- Dry mouth
- More cavities than other children
- Mouth sores
- Red, slick, tongue
- Yellow teeth or discolored teeth
Celiac vs. Gluten Sensitivity
Some people may not have full-blown Celiac disease but may still get symptoms after eating gluten such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, brain fog, or joint pain; an estimated 0.6-13% of the population have this condition, called non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Mouth symptoms in this population are not as widely reported, but may still appear as mouth ulcers or canker sores.
How to Treat Celiac Mouth Symptoms
A strict gluten-free diet is the most important treatment for Celiac disease, and will decrease canker sores and other mouth symptoms (although it won’t reverse earlier damage). Balancing the microbiome with dental probiotics and prebiotics may also improve symptoms, and L-glutamine, aloe vera juice, slippery elm, and zinc carnosine may help encourage healing of the oral lining.
REFERENCES
Nelson-Dooley, C. (2023, January 25). Recognizing early signs of celiac disease: mouth sores, burning tongue and more. https://www.drkarafitzgerald.com/2023/01/25/recognizing-early-signs-of-celiac-disease-mouth-sores-burning-tongue-and-more


 By
By







