
Food, Farming and Nutrition

Food, Farming and Nutrition
The Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are commonly known to benefit the body, but few understand how and why they do so. Found in many vitamins and minerals, such as zinc, copper, and vitamins C and E, antioxidants neutralize free radicals in the body.
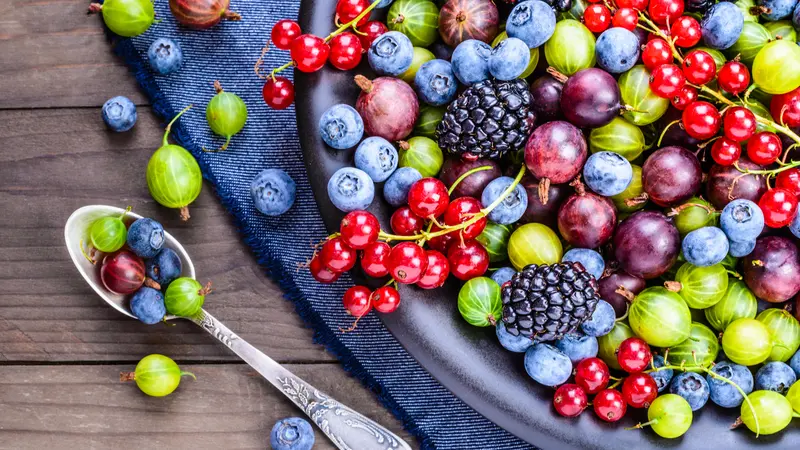
Free radicals are pervasive and volatile molecules that naturally occur in the body and cause damage to cells and the DNA they contain. Some free radicals are avoidable through lifestyle choices since they are generated through environmental triggers such as air pollution, cigarette smoke, and ultraviolet rays. Others are a natural cell byproduct and necessary to normal body functions. For instance, when the immune system is activated, it releases free radicals to attack damaged cells, invasive viruses, and bacteria. This natural production of free radicals creates a need for a natural production of antioxidants to keep them in check. Though the body can create its own antioxidants, they are also supplied through certain foods, including tomatoes, kale, blueberries, apples, onions, and green tea.
Antioxidants are not a specific component within vitamins and minerals, but rather a chemical property they contain. This chemical property counteracts free radicals through the contribution of electrons, warding off potential cell damage. Because of this, companies often advertise antioxidants as possessing the ability to slow aging, fight heart disease, preserve vision, and help cure cancer. However, studies have found that while diets containing antioxidant-rich foods may indeed benefit individuals, there is no evidence antioxidant supplements on their own are as beneficial. In order to attain the greatest health benefits from antioxidants, it is far more effective to consume a well-rounded diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
REFERENCES
Harvard Health Publishing. (2019, January 10). Understanding antioxidants. https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/understanding-antioxidants


 By
By







